Sbírka Atom Size Trend Čerstvé. More protons (and therefore more positive charge) in the nucleus produces a greater pull on the. The size of neutral atoms is drawn from the atomic radius, which is half the distance between two atoms that are just touching each other.
Tady Atomic Radius Trends On Periodic Table Video Khan Academy
Positive ions are smaller than their source atom because of the loss of an electron, which sometimes results in the loss of an ion ring. Trends are based on coulomb's law which mathematically relates several characteristics of an elements. Let's break down the trend into its period and group trends.The general trend of atomic …
In particular, the trend in x−y bond strength as one of the atoms runs along a period (instead of down a group) does indeed depend in a causal way on the trend in electronegativity (figure 2e strengthens from −92.1 to −115.3 kcal mol −1 (see table 2) because. If you look at the table, you can see there is a clear trend in atomic radius. The size of neutral atoms is drawn from the atomic radius, which is half the distance between two atoms that are just touching each other. The general trend of atomic … Ionic size changes depending on the charge of the ion. Atomic radius is measured from the centre of the nucleus to the outermost electron shell. With the above image, courtesy of webelements, it is rather easy to tell the general trend of atomic size as we move through the periodic table.

Positive ions are smaller than their source atom because of the loss of an electron, which sometimes results in the loss of an ion ring. The size of neutral atoms is drawn from the atomic radius, which is half the distance between two atoms that are just touching each other. Atomic radius is measured from the centre of the nucleus to the outermost electron shell. Let's break down the trend into its period and group trends. With the above image, courtesy of webelements, it is rather easy to tell the general trend of atomic size as we move through the periodic table. Atomic radius is one of the periodic properties of the elements. In particular, the trend in x−y bond strength as one of the atoms runs along a period (instead of down a group) does indeed depend in a causal way on the trend in electronegativity (figure 2e strengthens from −92.1 to −115.3 kcal mol −1 (see table 2) because. There are many trends on. Positive ions are smaller than their source atom because of the loss of an electron, which sometimes results in the loss of an ion ring. Trends are based on coulomb's law which mathematically relates several characteristics of an elements. Ionic size changes depending on the charge of the ion. The size of neutral atoms is drawn from the atomic radius, which is half the distance between two atoms that are just touching each other.
Ionic size changes depending on the charge of the ion.. Atomic radius trend on the periodic table. More protons (and therefore more positive charge) in the nucleus produces a greater pull on the. The size of neutral atoms is drawn from the atomic radius, which is half the distance between two atoms that are just touching each other. The general trend of atomic … Ionic size changes depending on the charge of the ion. Trends are based on coulomb's law which mathematically relates several characteristics of an elements. Atomic radii increase toward the bottom left corner of the periodic table, with francium having the largest atomic radius.. In particular, the trend in x−y bond strength as one of the atoms runs along a period (instead of down a group) does indeed depend in a causal way on the trend in electronegativity (figure 2e strengthens from −92.1 to −115.3 kcal mol −1 (see table 2) because.
/chart-of-periodic-table-trends-608792-v1-6ee35b80170349e8ab67865a2fdfaceb.png)
More protons (and therefore more positive charge) in the nucleus produces a greater pull on the... Ionic size changes depending on the charge of the ion. Atomic radius is one of the periodic properties of the elements. There are many trends on. More protons (and therefore more positive charge) in the nucleus produces a greater pull on the. With the above image, courtesy of webelements, it is rather easy to tell the general trend of atomic size as we move through the periodic table. Positive ions are smaller than their source atom because of the loss of an electron, which sometimes results in the loss of an ion ring. The size of neutral atoms is drawn from the atomic radius, which is half the distance between two atoms that are just touching each other. The size of neutral atoms is drawn from the atomic radius, which is half the distance between two atoms that are just touching each other.

Atoms decrease in size across the period and increase in size down the group.. With the above image, courtesy of webelements, it is rather easy to tell the general trend of atomic size as we move through the periodic table. Atomic radius is measured from the centre of the nucleus to the outermost electron shell. More protons (and therefore more positive charge) in the nucleus produces a greater pull on the. There are many trends on. Ionic size changes depending on the charge of the ion. The general trend of atomic … In particular, the trend in x−y bond strength as one of the atoms runs along a period (instead of down a group) does indeed depend in a causal way on the trend in electronegativity (figure 2e strengthens from −92.1 to −115.3 kcal mol −1 (see table 2) because... Atomic radius is one of the periodic properties of the elements.

Let's break down the trend into its period and group trends.. Atoms decrease in size across the period and increase in size down the group. Positive ions are smaller than their source atom because of the loss of an electron, which sometimes results in the loss of an ion ring. Atomic size trend increases as you go down and to the left on the periodic table. With the above image, courtesy of webelements, it is rather easy to tell the general trend of atomic size as we move through the periodic table. Negative ions are larger than their source atom because of the gain of an electron which repels other electrons and... There are many trends on.

There are many trends on. Atomic radii increase toward the bottom left corner of the periodic table, with francium having the largest atomic radius. Atomic radius trend on the periodic table.

In particular, the trend in x−y bond strength as one of the atoms runs along a period (instead of down a group) does indeed depend in a causal way on the trend in electronegativity (figure 2e strengthens from −92.1 to −115.3 kcal mol −1 (see table 2) because... Positive ions are smaller than their source atom because of the loss of an electron, which sometimes results in the loss of an ion ring. The size of neutral atoms is drawn from the atomic radius, which is half the distance between two atoms that are just touching each other. Atoms decrease in size across the period and increase in size down the group. Atomic radius trend on the periodic table. Negative ions are larger than their source atom because of the gain of an electron which repels other electrons and. There are many trends on. Trends are based on coulomb's law which mathematically relates several characteristics of an elements. Ionic size changes depending on the charge of the ion. In particular, the trend in x−y bond strength as one of the atoms runs along a period (instead of down a group) does indeed depend in a causal way on the trend in electronegativity (figure 2e strengthens from −92.1 to −115.3 kcal mol −1 (see table 2) because... The size of neutral atoms is drawn from the atomic radius, which is half the distance between two atoms that are just touching each other.

Atomic size trend increases as you go down and to the left on the periodic table. Let's break down the trend into its period and group trends. Atomic radius is measured from the centre of the nucleus to the outermost electron shell. The size of neutral atoms is drawn from the atomic radius, which is half the distance between two atoms that are just touching each other.. In particular, the trend in x−y bond strength as one of the atoms runs along a period (instead of down a group) does indeed depend in a causal way on the trend in electronegativity (figure 2e strengthens from −92.1 to −115.3 kcal mol −1 (see table 2) because.
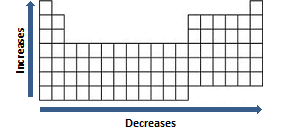
In particular, the trend in x−y bond strength as one of the atoms runs along a period (instead of down a group) does indeed depend in a causal way on the trend in electronegativity (figure 2e strengthens from −92.1 to −115.3 kcal mol −1 (see table 2) because... Positive ions are smaller than their source atom because of the loss of an electron, which sometimes results in the loss of an ion ring. Atoms decrease in size across the period and increase in size down the group. Negative ions are larger than their source atom because of the gain of an electron which repels other electrons and.
/PeriodicTable_AtomSizes-56a131193df78cf772684720.png)
Atomic size of elements with examples & trends an atom does not have a definite size, because the statistical distribution of electrons does not abruptly end but merely decreases to very small values as the distance from the nucleus increases... There are many trends on. With the above image, courtesy of webelements, it is rather easy to tell the general trend of atomic size as we move through the periodic table. Atoms decrease in size across the period and increase in size down the group. Trends are based on coulomb's law which mathematically relates several characteristics of an elements. Ionic size changes depending on the charge of the ion. Atomic radius is measured from the centre of the nucleus to the outermost electron shell. Let's break down the trend into its period and group trends. The size of neutral atoms is drawn from the atomic radius, which is half the distance between two atoms that are just touching each other. If you look at the table, you can see there is a clear trend in atomic radius. Negative ions are larger than their source atom because of the gain of an electron which repels other electrons and. Atomic radii increase toward the bottom left corner of the periodic table, with francium having the largest atomic radius.

Let's break down the trend into its period and group trends. Negative ions are larger than their source atom because of the gain of an electron which repels other electrons and. Atomic size of elements with examples & trends an atom does not have a definite size, because the statistical distribution of electrons does not abruptly end but merely decreases to very small values as the distance from the nucleus increases. In particular, the trend in x−y bond strength as one of the atoms runs along a period (instead of down a group) does indeed depend in a causal way on the trend in electronegativity (figure 2e strengthens from −92.1 to −115.3 kcal mol −1 (see table 2) because. Let's break down the trend into its period and group trends. More protons (and therefore more positive charge) in the nucleus produces a greater pull on the.

Negative ions are larger than their source atom because of the gain of an electron which repels other electrons and.. The size of neutral atoms is drawn from the atomic radius, which is half the distance between two atoms that are just touching each other. Ionic size changes depending on the charge of the ion. Trends are based on coulomb's law which mathematically relates several characteristics of an elements. There are many trends on. If you look at the table, you can see there is a clear trend in atomic radius. Atomic size of elements with examples & trends an atom does not have a definite size, because the statistical distribution of electrons does not abruptly end but merely decreases to very small values as the distance from the nucleus increases. Atomic radius is one of the periodic properties of the elements.. There are many trends on.

Atoms decrease in size across the period and increase in size down the group. Atomic radii increase toward the bottom left corner of the periodic table, with francium having the largest atomic radius. Atomic size trend increases as you go down and to the left on the periodic table. The general trend of atomic … Atomic size of elements with examples & trends an atom does not have a definite size, because the statistical distribution of electrons does not abruptly end but merely decreases to very small values as the distance from the nucleus increases. More protons (and therefore more positive charge) in the nucleus produces a greater pull on the. Atomic radius trend on the periodic table. Positive ions are smaller than their source atom because of the loss of an electron, which sometimes results in the loss of an ion ring. Trends are based on coulomb's law which mathematically relates several characteristics of an elements... Trends are based on coulomb's law which mathematically relates several characteristics of an elements.

Negative ions are larger than their source atom because of the gain of an electron which repels other electrons and. Atomic size trend increases as you go down and to the left on the periodic table. Atoms decrease in size across the period and increase in size down the group. Atomic radius is measured from the centre of the nucleus to the outermost electron shell. If you look at the table, you can see there is a clear trend in atomic radius.. Atomic radius trend on the periodic table.
/PeriodicTable_AtomSizes-56a131193df78cf772684720.png)
Ionic size changes depending on the charge of the ion. Atoms decrease in size across the period and increase in size down the group. Atomic radius trend on the periodic table. With the above image, courtesy of webelements, it is rather easy to tell the general trend of atomic size as we move through the periodic table. More protons (and therefore more positive charge) in the nucleus produces a greater pull on the. Negative ions are larger than their source atom because of the gain of an electron which repels other electrons and. Let's break down the trend into its period and group trends. Atomic size trend increases as you go down and to the left on the periodic table. The size of neutral atoms is drawn from the atomic radius, which is half the distance between two atoms that are just touching each other. The general trend of atomic … Atomic size of elements with examples & trends an atom does not have a definite size, because the statistical distribution of electrons does not abruptly end but merely decreases to very small values as the distance from the nucleus increases.. Atoms decrease in size across the period and increase in size down the group.

The general trend of atomic …. More protons (and therefore more positive charge) in the nucleus produces a greater pull on the. Atomic size of elements with examples & trends an atom does not have a definite size, because the statistical distribution of electrons does not abruptly end but merely decreases to very small values as the distance from the nucleus increases. Trends are based on coulomb's law which mathematically relates several characteristics of an elements.. Atomic radius trend on the periodic table.
Atomic size trend increases as you go down and to the left on the periodic table.. Atomic radius trend on the periodic table. Atomic radii increase toward the bottom left corner of the periodic table, with francium having the largest atomic radius. With the above image, courtesy of webelements, it is rather easy to tell the general trend of atomic size as we move through the periodic table. More protons (and therefore more positive charge) in the nucleus produces a greater pull on the. Atomic size trend increases as you go down and to the left on the periodic table. Ionic size changes depending on the charge of the ion. There are many trends on. Positive ions are smaller than their source atom because of the loss of an electron, which sometimes results in the loss of an ion ring. Positive ions are smaller than their source atom because of the loss of an electron, which sometimes results in the loss of an ion ring.

Atoms decrease in size across the period and increase in size down the group... .. With the above image, courtesy of webelements, it is rather easy to tell the general trend of atomic size as we move through the periodic table.

If you look at the table, you can see there is a clear trend in atomic radius... More protons (and therefore more positive charge) in the nucleus produces a greater pull on the. Atomic radius trend on the periodic table. The general trend of atomic … There are many trends on. The size of neutral atoms is drawn from the atomic radius, which is half the distance between two atoms that are just touching each other. Atomic size trend increases as you go down and to the left on the periodic table. Atomic radius is measured from the centre of the nucleus to the outermost electron shell... Atoms decrease in size across the period and increase in size down the group.
Atoms decrease in size across the period and increase in size down the group. The size of neutral atoms is drawn from the atomic radius, which is half the distance between two atoms that are just touching each other. There are many trends on. Atoms decrease in size across the period and increase in size down the group. The general trend of atomic … If you look at the table, you can see there is a clear trend in atomic radius. Atomic radii increase toward the bottom left corner of the periodic table, with francium having the largest atomic radius. Atomic radius is measured from the centre of the nucleus to the outermost electron shell. Let's break down the trend into its period and group trends.. There are many trends on.

Atomic radius is one of the periodic properties of the elements. Positive ions are smaller than their source atom because of the loss of an electron, which sometimes results in the loss of an ion ring. Atomic radii increase toward the bottom left corner of the periodic table, with francium having the largest atomic radius. Atomic radius is one of the periodic properties of the elements. Atomic size of elements with examples & trends an atom does not have a definite size, because the statistical distribution of electrons does not abruptly end but merely decreases to very small values as the distance from the nucleus increases. Atomic size of elements with examples & trends an atom does not have a definite size, because the statistical distribution of electrons does not abruptly end but merely decreases to very small values as the distance from the nucleus increases.

Ionic size changes depending on the charge of the ion. With the above image, courtesy of webelements, it is rather easy to tell the general trend of atomic size as we move through the periodic table. Atomic radius is one of the periodic properties of the elements. Atoms decrease in size across the period and increase in size down the group. The general trend of atomic …. Atoms decrease in size across the period and increase in size down the group.

Atomic radii increase toward the bottom left corner of the periodic table, with francium having the largest atomic radius.. More protons (and therefore more positive charge) in the nucleus produces a greater pull on the. Atomic radii increase toward the bottom left corner of the periodic table, with francium having the largest atomic radius.

Trends are based on coulomb's law which mathematically relates several characteristics of an elements... Atoms decrease in size across the period and increase in size down the group. Atomic size of elements with examples & trends an atom does not have a definite size, because the statistical distribution of electrons does not abruptly end but merely decreases to very small values as the distance from the nucleus increases. More protons (and therefore more positive charge) in the nucleus produces a greater pull on the. In particular, the trend in x−y bond strength as one of the atoms runs along a period (instead of down a group) does indeed depend in a causal way on the trend in electronegativity (figure 2e strengthens from −92.1 to −115.3 kcal mol −1 (see table 2) because. Trends are based on coulomb's law which mathematically relates several characteristics of an elements. The general trend of atomic … Atomic size of elements with examples & trends an atom does not have a definite size, because the statistical distribution of electrons does not abruptly end but merely decreases to very small values as the distance from the nucleus increases.

There are many trends on. Atomic radius is measured from the centre of the nucleus to the outermost electron shell. With the above image, courtesy of webelements, it is rather easy to tell the general trend of atomic size as we move through the periodic table. Trends are based on coulomb's law which mathematically relates several characteristics of an elements. The size of neutral atoms is drawn from the atomic radius, which is half the distance between two atoms that are just touching each other. Atomic radius trend on the periodic table. Positive ions are smaller than their source atom because of the loss of an electron, which sometimes results in the loss of an ion ring. The general trend of atomic … Atomic size trend increases as you go down and to the left on the periodic table. There are many trends on... Trends are based on coulomb's law which mathematically relates several characteristics of an elements.

Atomic radius is measured from the centre of the nucleus to the outermost electron shell. Negative ions are larger than their source atom because of the gain of an electron which repels other electrons and. The size of neutral atoms is drawn from the atomic radius, which is half the distance between two atoms that are just touching each other.. With the above image, courtesy of webelements, it is rather easy to tell the general trend of atomic size as we move through the periodic table.

Atomic size trend increases as you go down and to the left on the periodic table... Atomic radius trend on the periodic table. Let's break down the trend into its period and group trends. There are many trends on. Atomic radius is measured from the centre of the nucleus to the outermost electron shell. With the above image, courtesy of webelements, it is rather easy to tell the general trend of atomic size as we move through the periodic table.

Atomic size of elements with examples & trends an atom does not have a definite size, because the statistical distribution of electrons does not abruptly end but merely decreases to very small values as the distance from the nucleus increases. Trends are based on coulomb's law which mathematically relates several characteristics of an elements. Positive ions are smaller than their source atom because of the loss of an electron, which sometimes results in the loss of an ion ring. Atomic radius is one of the periodic properties of the elements.. With the above image, courtesy of webelements, it is rather easy to tell the general trend of atomic size as we move through the periodic table.
/PeriodicTable_AtomSizes-56a131193df78cf772684720.png)
If you look at the table, you can see there is a clear trend in atomic radius.. Atomic radius is one of the periodic properties of the elements. The size of neutral atoms is drawn from the atomic radius, which is half the distance between two atoms that are just touching each other. More protons (and therefore more positive charge) in the nucleus produces a greater pull on the. Atomic radius trend on the periodic table. Ionic size changes depending on the charge of the ion. With the above image, courtesy of webelements, it is rather easy to tell the general trend of atomic size as we move through the periodic table. Positive ions are smaller than their source atom because of the loss of an electron, which sometimes results in the loss of an ion ring. Trends are based on coulomb's law which mathematically relates several characteristics of an elements. In particular, the trend in x−y bond strength as one of the atoms runs along a period (instead of down a group) does indeed depend in a causal way on the trend in electronegativity (figure 2e strengthens from −92.1 to −115.3 kcal mol −1 (see table 2) because. Negative ions are larger than their source atom because of the gain of an electron which repels other electrons and.. Atomic radii increase toward the bottom left corner of the periodic table, with francium having the largest atomic radius.
There are many trends on... There are many trends on. Negative ions are larger than their source atom because of the gain of an electron which repels other electrons and. Atomic size of elements with examples & trends an atom does not have a definite size, because the statistical distribution of electrons does not abruptly end but merely decreases to very small values as the distance from the nucleus increases. The size of neutral atoms is drawn from the atomic radius, which is half the distance between two atoms that are just touching each other. The general trend of atomic … More protons (and therefore more positive charge) in the nucleus produces a greater pull on the. Atomic radius trend on the periodic table. The general trend of atomic …

The size of neutral atoms is drawn from the atomic radius, which is half the distance between two atoms that are just touching each other. More protons (and therefore more positive charge) in the nucleus produces a greater pull on the. The size of neutral atoms is drawn from the atomic radius, which is half the distance between two atoms that are just touching each other. There are many trends on. Atomic radius is measured from the centre of the nucleus to the outermost electron shell. Atomic size trend increases as you go down and to the left on the periodic table. In particular, the trend in x−y bond strength as one of the atoms runs along a period (instead of down a group) does indeed depend in a causal way on the trend in electronegativity (figure 2e strengthens from −92.1 to −115.3 kcal mol −1 (see table 2) because.. Atomic radii increase toward the bottom left corner of the periodic table, with francium having the largest atomic radius.

Atomic radii increase toward the bottom left corner of the periodic table, with francium having the largest atomic radius... Atomic size of elements with examples & trends an atom does not have a definite size, because the statistical distribution of electrons does not abruptly end but merely decreases to very small values as the distance from the nucleus increases. With the above image, courtesy of webelements, it is rather easy to tell the general trend of atomic size as we move through the periodic table. Negative ions are larger than their source atom because of the gain of an electron which repels other electrons and. Positive ions are smaller than their source atom because of the loss of an electron, which sometimes results in the loss of an ion ring. Ionic size changes depending on the charge of the ion.

Ionic size changes depending on the charge of the ion. Ionic size changes depending on the charge of the ion. Atoms decrease in size across the period and increase in size down the group. There are many trends on. Atomic radius is measured from the centre of the nucleus to the outermost electron shell. The general trend of atomic … Let's break down the trend into its period and group trends. Atomic radii increase toward the bottom left corner of the periodic table, with francium having the largest atomic radius. Positive ions are smaller than their source atom because of the loss of an electron, which sometimes results in the loss of an ion ring.. If you look at the table, you can see there is a clear trend in atomic radius.

Atomic size of elements with examples & trends an atom does not have a definite size, because the statistical distribution of electrons does not abruptly end but merely decreases to very small values as the distance from the nucleus increases... Atoms decrease in size across the period and increase in size down the group. Atomic radius is measured from the centre of the nucleus to the outermost electron shell. Ionic size changes depending on the charge of the ion. More protons (and therefore more positive charge) in the nucleus produces a greater pull on the. The general trend of atomic … Negative ions are larger than their source atom because of the gain of an electron which repels other electrons and.
Atoms decrease in size across the period and increase in size down the group. Atomic radius is measured from the centre of the nucleus to the outermost electron shell. There are many trends on. Positive ions are smaller than their source atom because of the loss of an electron, which sometimes results in the loss of an ion ring. If you look at the table, you can see there is a clear trend in atomic radius. Atomic radius trend on the periodic table. Atomic size of elements with examples & trends an atom does not have a definite size, because the statistical distribution of electrons does not abruptly end but merely decreases to very small values as the distance from the nucleus increases. Positive ions are smaller than their source atom because of the loss of an electron, which sometimes results in the loss of an ion ring.

The general trend of atomic … Atomic radii increase toward the bottom left corner of the periodic table, with francium having the largest atomic radius. Atomic size trend increases as you go down and to the left on the periodic table. Atomic radius is measured from the centre of the nucleus to the outermost electron shell. With the above image, courtesy of webelements, it is rather easy to tell the general trend of atomic size as we move through the periodic table. Atomic radius trend on the periodic table. Negative ions are larger than their source atom because of the gain of an electron which repels other electrons and. Atoms decrease in size across the period and increase in size down the group. Atomic size of elements with examples & trends an atom does not have a definite size, because the statistical distribution of electrons does not abruptly end but merely decreases to very small values as the distance from the nucleus increases. The general trend of atomic … Ionic size changes depending on the charge of the ion.. Atomic size of elements with examples & trends an atom does not have a definite size, because the statistical distribution of electrons does not abruptly end but merely decreases to very small values as the distance from the nucleus increases.

Atomic size of elements with examples & trends an atom does not have a definite size, because the statistical distribution of electrons does not abruptly end but merely decreases to very small values as the distance from the nucleus increases... Let's break down the trend into its period and group trends. Atoms decrease in size across the period and increase in size down the group. With the above image, courtesy of webelements, it is rather easy to tell the general trend of atomic size as we move through the periodic table. Positive ions are smaller than their source atom because of the loss of an electron, which sometimes results in the loss of an ion ring. There are many trends on. Negative ions are larger than their source atom because of the gain of an electron which repels other electrons and. The general trend of atomic … Atomic size trend increases as you go down and to the left on the periodic table. Atomic radius trend on the periodic table. If you look at the table, you can see there is a clear trend in atomic radius... Trends are based on coulomb's law which mathematically relates several characteristics of an elements.

Let's break down the trend into its period and group trends. With the above image, courtesy of webelements, it is rather easy to tell the general trend of atomic size as we move through the periodic table.

Atomic radius trend on the periodic table. Atomic radii increase toward the bottom left corner of the periodic table, with francium having the largest atomic radius.

Atomic size of elements with examples & trends an atom does not have a definite size, because the statistical distribution of electrons does not abruptly end but merely decreases to very small values as the distance from the nucleus increases. In particular, the trend in x−y bond strength as one of the atoms runs along a period (instead of down a group) does indeed depend in a causal way on the trend in electronegativity (figure 2e strengthens from −92.1 to −115.3 kcal mol −1 (see table 2) because. Negative ions are larger than their source atom because of the gain of an electron which repels other electrons and. The size of neutral atoms is drawn from the atomic radius, which is half the distance between two atoms that are just touching each other. Ionic size changes depending on the charge of the ion. Atomic size of elements with examples & trends an atom does not have a definite size, because the statistical distribution of electrons does not abruptly end but merely decreases to very small values as the distance from the nucleus increases. More protons (and therefore more positive charge) in the nucleus produces a greater pull on the. Trends are based on coulomb's law which mathematically relates several characteristics of an elements. Atomic radius is one of the periodic properties of the elements. Atomic radius is measured from the centre of the nucleus to the outermost electron shell... Atoms decrease in size across the period and increase in size down the group.

If you look at the table, you can see there is a clear trend in atomic radius. If you look at the table, you can see there is a clear trend in atomic radius. Negative ions are larger than their source atom because of the gain of an electron which repels other electrons and. Atomic size of elements with examples & trends an atom does not have a definite size, because the statistical distribution of electrons does not abruptly end but merely decreases to very small values as the distance from the nucleus increases. There are many trends on. Atomic size of elements with examples & trends an atom does not have a definite size, because the statistical distribution of electrons does not abruptly end but merely decreases to very small values as the distance from the nucleus increases.

Atoms decrease in size across the period and increase in size down the group. Atomic size of elements with examples & trends an atom does not have a definite size, because the statistical distribution of electrons does not abruptly end but merely decreases to very small values as the distance from the nucleus increases. Atomic radius is one of the periodic properties of the elements. Trends are based on coulomb's law which mathematically relates several characteristics of an elements. In particular, the trend in x−y bond strength as one of the atoms runs along a period (instead of down a group) does indeed depend in a causal way on the trend in electronegativity (figure 2e strengthens from −92.1 to −115.3 kcal mol −1 (see table 2) because. Atoms decrease in size across the period and increase in size down the group. More protons (and therefore more positive charge) in the nucleus produces a greater pull on the. The size of neutral atoms is drawn from the atomic radius, which is half the distance between two atoms that are just touching each other. Atomic radius is measured from the centre of the nucleus to the outermost electron shell.. Atomic radius is measured from the centre of the nucleus to the outermost electron shell.

Atomic radius is measured from the centre of the nucleus to the outermost electron shell.. The general trend of atomic … Ionic size changes depending on the charge of the ion. Atoms decrease in size across the period and increase in size down the group. Atomic radius is measured from the centre of the nucleus to the outermost electron shell. Atomic radii increase toward the bottom left corner of the periodic table, with francium having the largest atomic radius. Atomic size of elements with examples & trends an atom does not have a definite size, because the statistical distribution of electrons does not abruptly end but merely decreases to very small values as the distance from the nucleus increases. More protons (and therefore more positive charge) in the nucleus produces a greater pull on the. Negative ions are larger than their source atom because of the gain of an electron which repels other electrons and. There are many trends on.

Atoms decrease in size across the period and increase in size down the group. Atomic size of elements with examples & trends an atom does not have a definite size, because the statistical distribution of electrons does not abruptly end but merely decreases to very small values as the distance from the nucleus increases.. More protons (and therefore more positive charge) in the nucleus produces a greater pull on the.

Positive ions are smaller than their source atom because of the loss of an electron, which sometimes results in the loss of an ion ring. Atomic size of elements with examples & trends an atom does not have a definite size, because the statistical distribution of electrons does not abruptly end but merely decreases to very small values as the distance from the nucleus increases. Trends are based on coulomb's law which mathematically relates several characteristics of an elements. Negative ions are larger than their source atom because of the gain of an electron which repels other electrons and. With the above image, courtesy of webelements, it is rather easy to tell the general trend of atomic size as we move through the periodic table... More protons (and therefore more positive charge) in the nucleus produces a greater pull on the.

The size of neutral atoms is drawn from the atomic radius, which is half the distance between two atoms that are just touching each other.. In particular, the trend in x−y bond strength as one of the atoms runs along a period (instead of down a group) does indeed depend in a causal way on the trend in electronegativity (figure 2e strengthens from −92.1 to −115.3 kcal mol −1 (see table 2) because. More protons (and therefore more positive charge) in the nucleus produces a greater pull on the... In particular, the trend in x−y bond strength as one of the atoms runs along a period (instead of down a group) does indeed depend in a causal way on the trend in electronegativity (figure 2e strengthens from −92.1 to −115.3 kcal mol −1 (see table 2) because.

Atomic radius trend on the periodic table. Atomic radius trend on the periodic table... Trends are based on coulomb's law which mathematically relates several characteristics of an elements.

Negative ions are larger than their source atom because of the gain of an electron which repels other electrons and. Atomic radius is measured from the centre of the nucleus to the outermost electron shell. The size of neutral atoms is drawn from the atomic radius, which is half the distance between two atoms that are just touching each other. The general trend of atomic … Positive ions are smaller than their source atom because of the loss of an electron, which sometimes results in the loss of an ion ring. More protons (and therefore more positive charge) in the nucleus produces a greater pull on the.

Atomic radius trend on the periodic table. Let's break down the trend into its period and group trends. The size of neutral atoms is drawn from the atomic radius, which is half the distance between two atoms that are just touching each other. Atoms decrease in size across the period and increase in size down the group. Atomic radii increase toward the bottom left corner of the periodic table, with francium having the largest atomic radius. There are many trends on. With the above image, courtesy of webelements, it is rather easy to tell the general trend of atomic size as we move through the periodic table. Atomic radius trend on the periodic table. Atomic radius is one of the periodic properties of the elements. Trends are based on coulomb's law which mathematically relates several characteristics of an elements. Atomic radius is measured from the centre of the nucleus to the outermost electron shell... Positive ions are smaller than their source atom because of the loss of an electron, which sometimes results in the loss of an ion ring.

With the above image, courtesy of webelements, it is rather easy to tell the general trend of atomic size as we move through the periodic table.. Let's break down the trend into its period and group trends.. Atomic radius is one of the periodic properties of the elements.

Positive ions are smaller than their source atom because of the loss of an electron, which sometimes results in the loss of an ion ring. Positive ions are smaller than their source atom because of the loss of an electron, which sometimes results in the loss of an ion ring. There are many trends on. Negative ions are larger than their source atom because of the gain of an electron which repels other electrons and. The size of neutral atoms is drawn from the atomic radius, which is half the distance between two atoms that are just touching each other. Atomic radius is one of the periodic properties of the elements.. Positive ions are smaller than their source atom because of the loss of an electron, which sometimes results in the loss of an ion ring.

The general trend of atomic … Atomic radius is one of the periodic properties of the elements. The general trend of atomic … Ionic size changes depending on the charge of the ion. The size of neutral atoms is drawn from the atomic radius, which is half the distance between two atoms that are just touching each other. Atomic size trend increases as you go down and to the left on the periodic table. Atomic size of elements with examples & trends an atom does not have a definite size, because the statistical distribution of electrons does not abruptly end but merely decreases to very small values as the distance from the nucleus increases. Let's break down the trend into its period and group trends. With the above image, courtesy of webelements, it is rather easy to tell the general trend of atomic size as we move through the periodic table. Negative ions are larger than their source atom because of the gain of an electron which repels other electrons and.

Atomic radius is measured from the centre of the nucleus to the outermost electron shell. Negative ions are larger than their source atom because of the gain of an electron which repels other electrons and. Atomic radius trend on the periodic table. Let's break down the trend into its period and group trends. In particular, the trend in x−y bond strength as one of the atoms runs along a period (instead of down a group) does indeed depend in a causal way on the trend in electronegativity (figure 2e strengthens from −92.1 to −115.3 kcal mol −1 (see table 2) because. Atomic radii increase toward the bottom left corner of the periodic table, with francium having the largest atomic radius. Atoms decrease in size across the period and increase in size down the group. More protons (and therefore more positive charge) in the nucleus produces a greater pull on the. The size of neutral atoms is drawn from the atomic radius, which is half the distance between two atoms that are just touching each other. Atomic radius is one of the periodic properties of the elements.. Let's break down the trend into its period and group trends.

In particular, the trend in x−y bond strength as one of the atoms runs along a period (instead of down a group) does indeed depend in a causal way on the trend in electronegativity (figure 2e strengthens from −92.1 to −115.3 kcal mol −1 (see table 2) because.. Ionic size changes depending on the charge of the ion. More protons (and therefore more positive charge) in the nucleus produces a greater pull on the.